The deadline for Google’s Mobile-First Indexing update is around the corner as March 2021 is just a month away now. In case you haven’t made the necessary changes yet, you still have time to get ready for this Google’s major update of 2021. However, if you are planning to ignore this update, then get ready for a huge loss in your site’s ranking and traffic.
List of Topics Covered in This Post
- Major Announcements by Google on Mobile-First Indexing
- What Is Mobile-First Indexing?
- Why Is Google Shifting to Mobile-First Indexing?
- Why Is Google’s Mobile-First Indexing Important?
- How to Find Out If My Website Is on Mobile-First Indexing?
- How to Enable Mobile-First Indexing for My Site?
- What Kinds of Websites Don’t Need Changes for Mobile-First Indexing?
- Things You Should Know About Mobile-First Indexing
- What are the Best Practices to get ready for Mobile-First Indexing?
Major Announcements by Google on Mobile-First Indexing
Mobile-First Indexing is something on which Google is working for around five years. In 2016, Google talked about mobile-first indexing openly for the first time. At that time, it acknowledged that, “Today, most people are searching on Google using a mobile device”. In response to the changing search behavior of people, Google said –
“To make our results more useful, we’ve begun experiments to make our index mobile-first. Although our search index will continue to be a single index of websites and apps, our algorithms will eventually primarily use the mobile version of a site’s content to rank pages from that site.”
Besides, Google also provided a few tips on what to do if their website configuration is different across mobile and desktop.
Though Google intended to roll out this update by September 2020, it rescheduled the deadline for mobile-first indexing to the end of March 2021 for the obvious reasons – the COVID-19 pandemic.
In the light of the COVID-19 worldwide outbreak, Google announced, “Our initial plan was to enable mobile-first indexing for all sites in Search in September 2020. We realize that in these uncertain times, it’s not always easy to focus on work as otherwise, so we’ve decided to extend the timeframe to the end of March 2021.”
What’s more, Google has already enabled mobile-first indexing for all new websites and also for most currently crawled websites. To the surprise of many, more than 70% of websites in search have already migrated to mobile-first.
What Is Mobile-First Indexing?
Mobile-first indexing means that Google will use only mobile versions of websites for indexing purposes, instead of the desktop version that Google preferred previously.
In other words, if you have separate versions of your website for mobile and desktop, Google will index and rank the mobile version of your site.
Are you wondering why Google is making this huge shift? You might not be alone. So, before sharing what you should do, let’s ponder upon why Google is doing it now.
Why Is Google Shifting to Mobile-First Indexing?
The number of people accessing the internet via their mobile devices is growing rapidly. The trend is likely to continue.
If we take a look at the 2020 data of different countries, you can easily notice the increasing popularity and usage of smartphones.
- In India, 80% of total (500 million) internet users go online through their mobile devices.
- In the US, Americans have the highest mobile broadband subscription penetration rate of 97.1%. The mobile share of total digital minutes was recorded to be 79%.
- In Europe, the highest mobile broadband subscription penetration rate is 93.6%.
- In Australia, 91% of people own smartphones, and smartphone penetration has grown from 76% to 91% in the last six years.
Mobile searches are also bound to increase because people in developing countries have much easy access to smartphones than desktops. While India is already famous for being a bigger market for mobile-first population, other countries like Nigeria, Ghana, and Kenya also registered tremendous growth in internet traffic coming from mobile devices. Besides, in most African markets, mobile devices account for more than half of the web traffic.
Whether it is news, music, social media, entertainment, or checking e-mails, people now prefer their mobile devices. In the future, the preference for mobile devices over desktops is unlikely to change.
Google is always in the pursuit of finding ways that make the lives of people easier. It doesn’t matter if it is a small thing or big, it wants to serve the best. That’s why as the behavior and preferences of people change, Google also changes its way of serving. This time, it is doing this by shifting to mobile-first indexing.
Why Is Google’s Mobile-First Indexing Important?
Every reputable business, regardless of its size, gives the topmost priority to its customers. You will have no choice after March 2021. Google is going to enable mobile-first indexing for your business website.
If your website is not ready for mobile-first indexing, you are going to witness a substantial loss in terms of ranking and customer experience.
If you don’t want to turn away your potential customers or hurt your website’s ranking, you should pay attention to this Google update and do everything in your capacity so that your website and its traffic don’t suffer the consequences.
How to Find Out If My Website Is on Mobile-First Indexing?
After hearing this update, a lot of website owners are curious to know if their site is on mobile-first indexing. If you are one of them, here is a simple breakdown of the Google’s mobile-first-indexing checking process.
1. Check Notifications from Google Search Console
When Google enables mobile-first indexing for a website, it sends a notification. So, first of all, you should check the messages in your Google Search Console.
Here is what the notification for Enabled Mobile-First Indexing looks like:
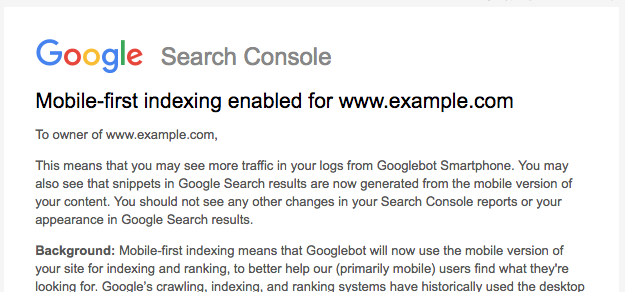
Image Source: Google Search Central
2. Use URL Inspection Tool to see if your website is on mobile-first indexing.
To see the current index status, follow the below-given steps.
Steps to Check If Your Site is on Mobile-First Indexing
Step 1: Open the Google Search Console’s URL Inspection Tool.
Step 2: Enter the complete URL of your site.
Step 3: Check the Results and look for ‘Crawled as’ in the tabular report.
Here is what you will be seeing while checking the indexing status for your site:
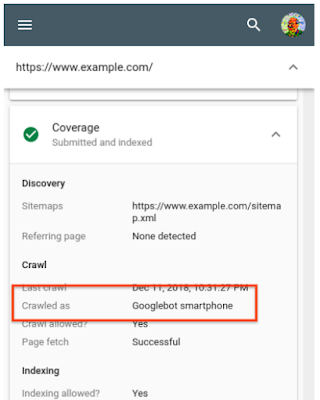
Image Source: Google Search Central
If your site is crawled by Googlebot smartphone, it means your site is on mobile-first indexing. However, if your site is crawled by Googlebot Desktop, your site is not being indexed for mobile version yet.
How to Enable Mobile-first Indexing for My Site?
You cannot enable mobile-first indexing yourself. Just wait and Google will do it as soon as it recognizes that your site is ready for migration. Or, just wait a bit more because Google will enable mobile-first indexing for all sites by the end of March 2021.
What Kinds of Websites Don’t Need Changes For Mobile-First Indexing?
Google has already informed that if your website is already responsive or dynamic serving and has the equivalent primary content and markup across mobile and desktop, you don’t have to worry about changing anything.
However, if it is not, you need to make some changes so that your site’s traffic, ranking, and user experience don’t get affected.
Things You Should Know About Mobile-First Indexing
- Mobile-First Indexing is not the same as Mobile-Usability.
Both ‘mobile-usability and ‘mobile-first indexing’ are completely different concepts. Even if your content doesn’t pass the mobile usability test, Google still can shift your site to mobile-first indexing. Similarly, even if your site passes the mobile usability test, it does not mean it is being indexed as mobile-first.
- Google Search uses only one index. There are no separate indexes for Mobile and Desktop.
Previously, Google used the Desktop Indexing. Currently, Google uses Mobile-First Indexing. This means, there was, is, and will be only one index.
- Once your site is enabled for mobile-first indexing, you cannot disable it.
Google is not providing site owners with a choice. Once your site is moved to mobile-first indexing, there is no going back. So, make up your mind and discuss the importance of mobile-first indexing with your teams of website developers and designers.
- You should keep the same content on your site’s mobile as well as desktop version.
Since the mobile version will be indexed and ranked, your site visitors will get to see and read the information available on your site’s mobile version. If you have less content, blocked or low-quality images, or fewer services or products on the mobile version, the experience of your visitors will be hugely affected. That, in turn, will affect your site’s ranking and credibility in the eyes of Google.
- Page Speed matters and you must not ignore it.
Page Speed plays a big role in negative bounce rates. 53% of mobile users abandon a site if the page takes more than 3 seconds to load. A 2-second delay in load time can skyrocket the abandonment rates up to 87%. Plus, a very slow site can be a negative Google ranking factor. So, if your site’s page speed is slow, work on it.
What Are the Best Practices to Get Ready for Mobile-First Indexing?
Since Google will be using 100% mobile-first indexing by the end of March 2021, you need to optimize your site accordingly, especially if your site is not responsive or dynamic serving type.
Here are some of the best practices that Google has shared over the past months to get ready for mobile-first indexing:
Ensure that Googlebot can see the full content and all resources on your site’s mobile version.
- Use the same robots meta tags on mobile and desktop versions.
- Avoid lazy-loading your primary content based on user interactions, such as swiping, clicking, and typing.
- Follow lazy-loading best practices especially for loading images and videos.
- Don’t disallow crawling of URLs with robots.txt file. For instance, if you block the URLs of .css files, it will prevent Googlebot from rendering your pages effectively.
Ensure that primary content is the same on mobile and desktop versions.
- If your mobile version has less content than desktop, update your mobile version in a way that its primary content is equivalent.
- Use the headings with the same words (clear and meaningful) on both versions; otherwise, it may negatively impact the visibility of your page in Search.
- Use the same heading tag for the same headings.
- If you implement Data Highlighter, train it on your mobile site and regularly check for extraction errors.
Ensure that your images and videos are optimized.
- Don’t use too small images or the ones with the low resolution on the mobile version. Low-quality images are not selected for inclusion in Google Images.
- Add alt attribute with meaningful text in the image tag. It’s a bad practice to leave the alt attribute empty or not using the alt attribute at all.
- Use the same image URLs (that don’t change every time the page loads) on the mobile version as you used on the desktop. Do the same for videos as well.
- Use the same video structured data and correct URLs for videos on both versions.
- Put your videos in supported formats and tags.
Other Key Considerations
- Keep the same descriptive title and meta description across the desktop and mobile versions.
- Follow the Better Ads Standard while displaying ads on mobile devices.
- The error page status should be the same on both versions.
- There should be no fragment URLs in the mobile version.
- Desktop versions with different contents should have equivalent mobile versions.
- Verify through Google Search Console if data and messages are accessible in both versions.
- While using hreflang link elements, link between mobile and desktop URLs separately.
- Use rel=canonical and rel=alternate link elements correctly between both versions.
Conclusion
By now, you can easily gather that the overall aim is that your website should provide the same experience across mobile and desktop versions. If your website designers find it tempting to improve mobile usability by removing content, it can lead to significant traffic losses. Since mobile-first indexing update is not a choice and it is not going anywhere, you should discuss all the issues in your site’s mobile version with your team, and justify why it is critical to implement the best practices before issues start arising with your site’s ranking, traffic, and ultimately revenue.

